Reflective Supervision for coaches & other professions
What is
Supervision is a space for regular protected time for facilitated, in-depth reflection on your coaching practice along with experiential learning. It is
Although this is directed to coaches Maeve Finch also supervises other helping professionals
Just as a coach can help
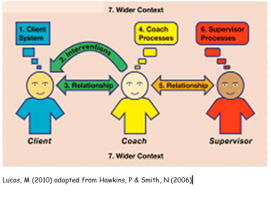
This is combined with the work of Proctor, B. Group Supervision: A Guide to Creative Practice (2000) who regards supervision as ‘a co-operative exercise in accountability’. Proctor divides supervision into the following three areas:
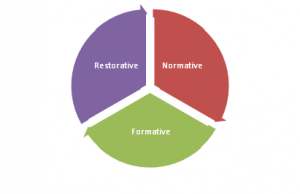
• Normative – the supervisor accepts and shares with the supervisee the responsibility for ensuring that the supervisee’s work is professional and ethical.
• Formative – the supervisor acts to provide feedback and/or direction that will enable the supervisee to develop the skills, knowledge and personal attitudes
• Restorative / Supportive – the supervisor listens, supports and draws the supervisee’s attention to any personal issues, doubts, ethical issues, and any other supervisee issues that arise. These three factors develop in coaches an in-depth reflection of their coaching practice along with their own experimental learning.
Supervision can be arranged with Maeve Finch of Total Focus in the following manner:
Individual supervision 1-1 basis
Group supervision usually a group of coaches who already has a high level of trust amongst themselves – approx. 4-5 coaches
What is a supervisee? A supervisee is a person or coach who comes to the supervisor for supervision.
Why should I bother with supervision? Supervision is regarded as best practise. Most supervisees who attend regular supervision sessions are aware of an added bonus to themselves as coaches, to their coaching practise and their clients. Other benefits can be found in a report published by Hawkins, P.; Schwenk G., Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD ) 2006 called Coaching supervision Maximising the Potential for Coaching .
Benefits of supervision for supervisees
• It helps supervisees to identify their strengths and weaknesses
• Keeps supervisees aware of ethical and professional issues
• It identifies if any of the work being undertaken by the supervisee is starting a parallel process within themselves •
It keeps supervisees up to date with changes within the industry
• Enhances your own practice by challenging you as a coach • Helps the supervisee to become more self-aware.
How often should I attend supervision? As often as you think you need to. All coaching associations in Ireland including the AC, ICF
Maeve Finch of Total Focus Maeve was awarded a Higher Diploma from Middlesex University studying with Dr. Michael Carroll, (one of the most
“Supervision is gathering the treasures of the past into the competencies of the present for the wellbeing of the future”
The Soul of Supervision Carroll M 2010
